Describe the Cellular Basis for Immunological Memory
Human immunological memory is the key distinguishing hallmark of the adaptive immune system and plays an important role in the prevention of morbidity and the severity of infection. Primed spleen cells taken from CBA or CBAT6T6 mice were cultured for 5.

Pdf Immunological Memory Cells
The activated lymphoblasts can be isolated by density gradient centrifugation and when cultured in the absence of autoantigen they will revert back to quiescent 2 memory populations.

. The thymus is known to play a central part in the establishment of immunological competence. Long-lived antibody secreting cells ASCs are responsible for maintaining antibody levels in peripheral blood. Describe the cellular basis for self-tolerance.
Recent findings have shown that group 2 innate lymphoid cells ILC2s can be classified as immunological memory cells. Immunological memory is the ability of the immune system to respond more rapidly and effectively to pathogens that have been encountered previously and reflects the preexistence of a clonally expanded population of antigen-specific lymphocytes. This follows from a demonstration that cells from spleens of mice primed with sheep erythrocytes are capable of inducing normally unresponsive bone marrow cells to produce specific antibody.
Describe the relationship between linkage groups andchromosomes. Moreover these cells share many features with memory T lymphocytes and memory NK cells. Describe the cellular basis for immunological memory.
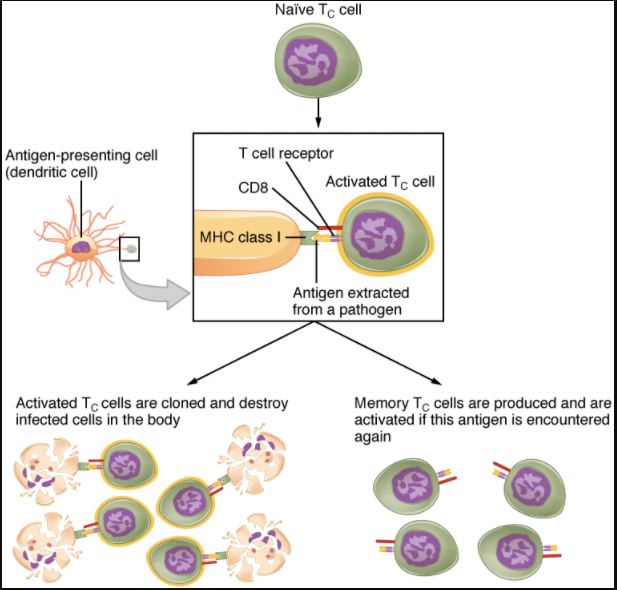
As already discussed one of the major features of an adaptive immune response is the development of immunological memory. Thus immunological memory is generated during the primary response in part because the proliferation of antigen-stimulated naïve cells creates many memory cellsa process known as clonal expansionand in part because memory cells are able to respond more sensitively and rapidly to the same antigen than do naïve cells. B-cells and immunological memory Not all B-cells generated by clonal selection mature into antibody-producing plasma cells.
Publication types Research Support Non-US. In vitro EAO effector T cells destroy syngeneic Sertoli cell monolayers. Describe the cellular basis for immunological memory o Immunological memory.
The Cellular Basis of Immunological Memory. Some activate B cells dont become antibody-producing plasma cells but persist as long-lived but non-proliferating memory cells. Figure 120 The course of a typical antibody response.
The differentiation system of T cell memory has been clarified using mouse models. Responsible for the long-term protection that a prior infection or vaccination provides against many diseases o Secondary immune response relies on the reservoir of T and B memory cells generated following initial exposure to an antigen Because these cells are long-lived they. Explain how B cells are activated.
Naive and memory T cells differ in that memory T cells give a more vigorous and sustained response than naive T cells. At the second time of infection these cells are stimulated by the same antigen they have memory of and then rapidly differentiate into antibody-producing plasma cells. During a primary adaptive immune response both memory T cells and effector T cells are generated.
Cellular basis of immunological self tolerance. Generation of pre-existing memory B cell and T cell pools is thus the key for maintaining protective immunity to seasonal pandemic and avian influenza viruses. It is concluded that IgM immunological memory is carried by cells which are not producing plaques and reasons are discussed for supposing that memory cells and antibody-forming cells belong to separate cell lineages.
Perhaps the most important consequence of an adaptive immune response is the establishment of a state of immunological memory. The Immunological Basis of Liver Allograft Rejection Front Immunol. ON THE CELLULAR BASIS OF IMMUNOLOGICAL T-CELL MEMORY.
The cellular basis of immunological memory is the clonal expansion and clonal differentiation of cells specific for the eliciting antigen and it is therefore entirely antigen specific. The results show that memory cells can be derived from activated T cells and persist in the absence of antigen for at least 13 weeks. Memory T cells are long-lived and can even persist for a lifetime.
Explain how the humoral response is provoked. The cellular foundation of immunological memory resides in the existence of memory lymphocytes which carry the memory of a previous exposure to an antigen along with an altered and enhanced. And unlike most effector cells which die within.
Persistent and durable immunological memory forms the basis of any successful vaccination protocol. Memory T cells are long-lived and can even persist for a lifetime. Cellular and humoral regulation.
The Cellular Basis of Immunological Memory As already discussed one of the major features of an adaptive immune response is the development of immunological memory. Govt MeSH terms Animals. During a primary adaptive immune response both memory T cells and effector T cells are generated.
Immunological memory and antibody formation appear to be properties of different cell lines. This immunological memory presumably involves specific cells but it is not known whether it involves generation of an increased number of cells or increased synthetic or some other ability in. A significant proportion remain in the body for many years as memory cells Ratajczak et al 2018.
The following three articles describe experiments aimed at. Describe the cellular basis for immunological memory. On the basis of number of experiment we can conclude that 4 H ions must flow into the matrix back t.
Please describe the competing interests. Generation of pre-existing memory B cell and T cell pools is thus the key for maintaining protective immunity to seasonal pandemic and avian influenza viruses. Long-lived antibody secreting cells AS.
Diagram and label the structure of an antibody and explain how this structure allows antibodies to perform the following functions. Here the current understanding of the cellular basis of immune memory is reviewed and the relative contributions made to protective immunity by memory and effector T and B cells are examined. Persistent and durable immunological memory forms the basis of any successful vaccination protocol.
Activated T-cells have a variety of effector mechanisms including direct T-cell mediated damage to bile ducts endothelium and hepatocytes and indirect effects through cytokine production and recruitment of tissue-destructive inflammatory cells.
How Do Immune Cells Of Animals Recognize Foreign Cells Ppt Download

Immune System Haixu Tang School Of Informatics Human Lymphoid Organs Ppt Download

Translating Innate Immunity Into Immunological Memory Implications For Vaccine Development Cell
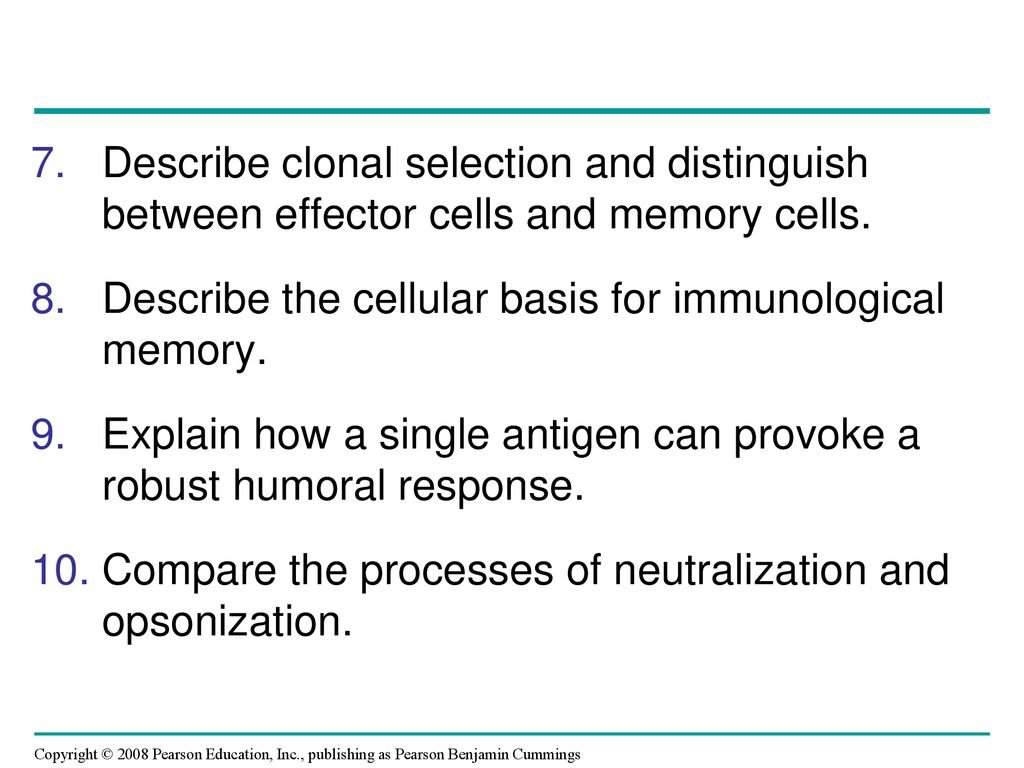
Frontiers T Cell Memory In Infection Cancer And Autoimmunity Immunology

Immunologic Memory An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Cellular Basis Of Immunity Ppt Download

Trained Immunity A Program Of Innate Immune Memory In Health And Disease Abstract Europe Pmc

Pdf Immunological Memory In Humans
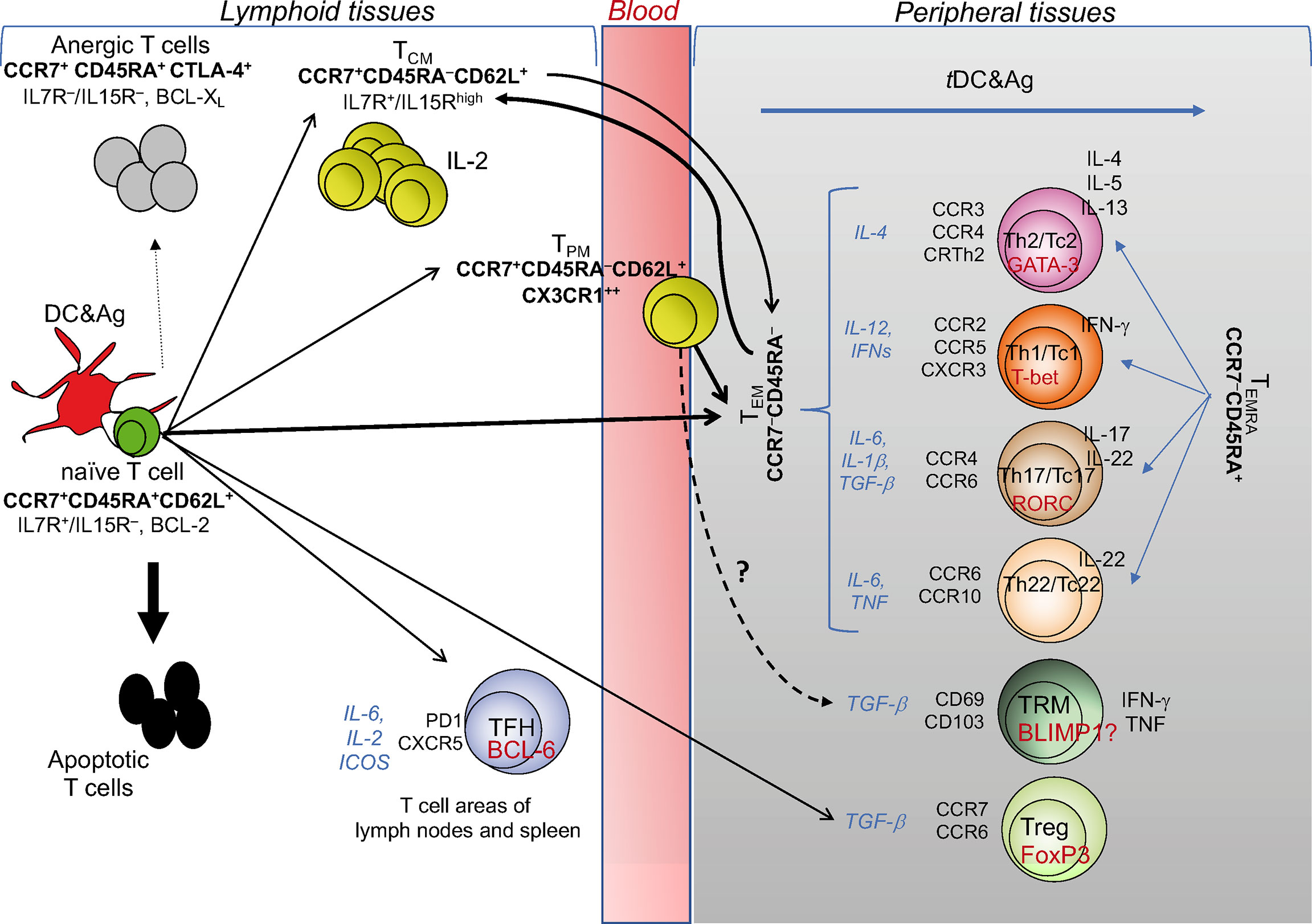
7 3 The Adaptive Immune Response T Lymphocytes And Their Functional Types Fundamentals Of Anatomy And Physiology

Translating Innate Immunity Into Immunological Memory Implications For Vaccine Development Cell
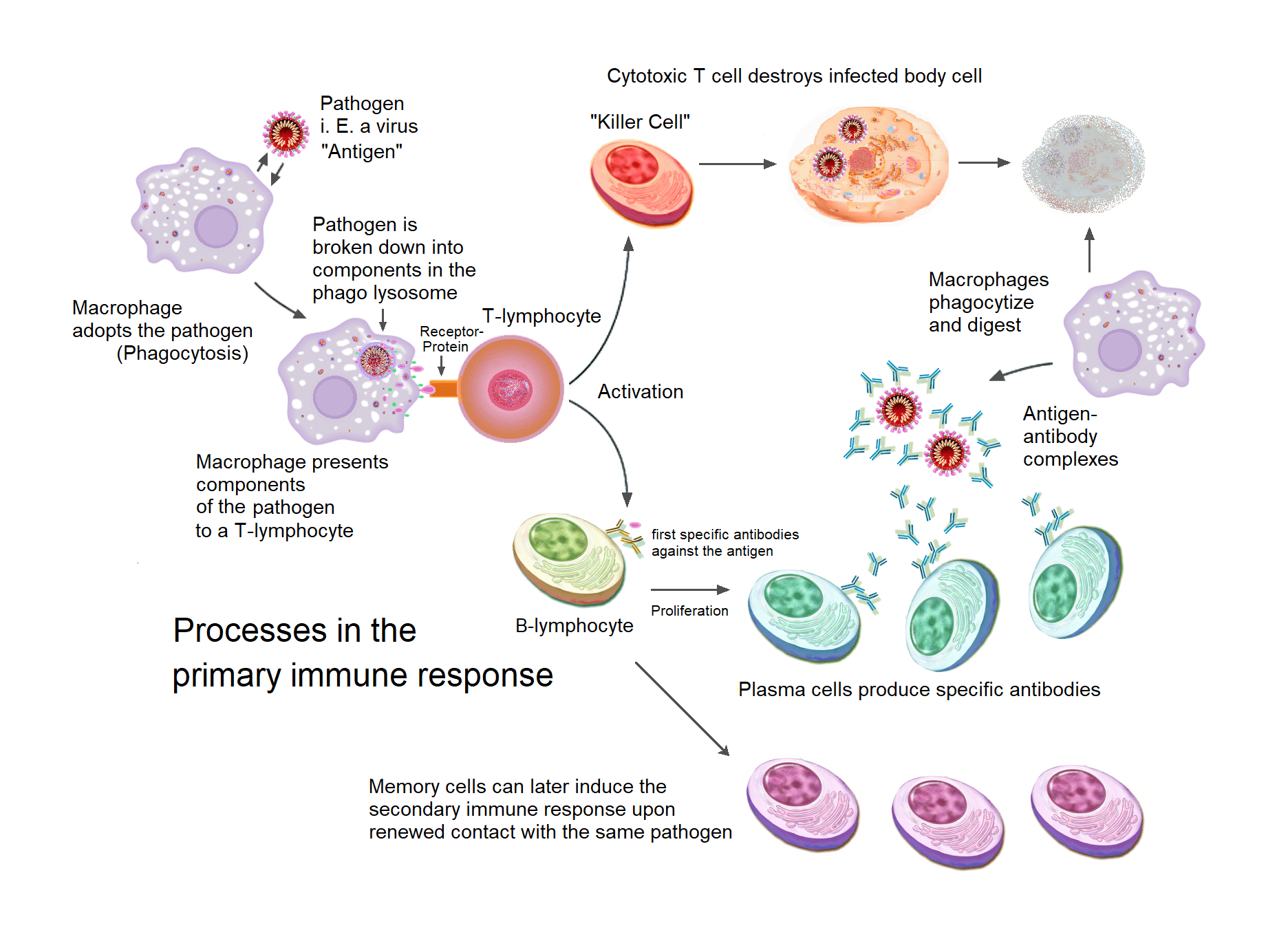
Primary And Secondary Responses Memory Cells Teachmephysiology

Chapter 43 The Immune System Ppt Download

Helper T Cells A Response To Nearly All Antigens Ppt Download
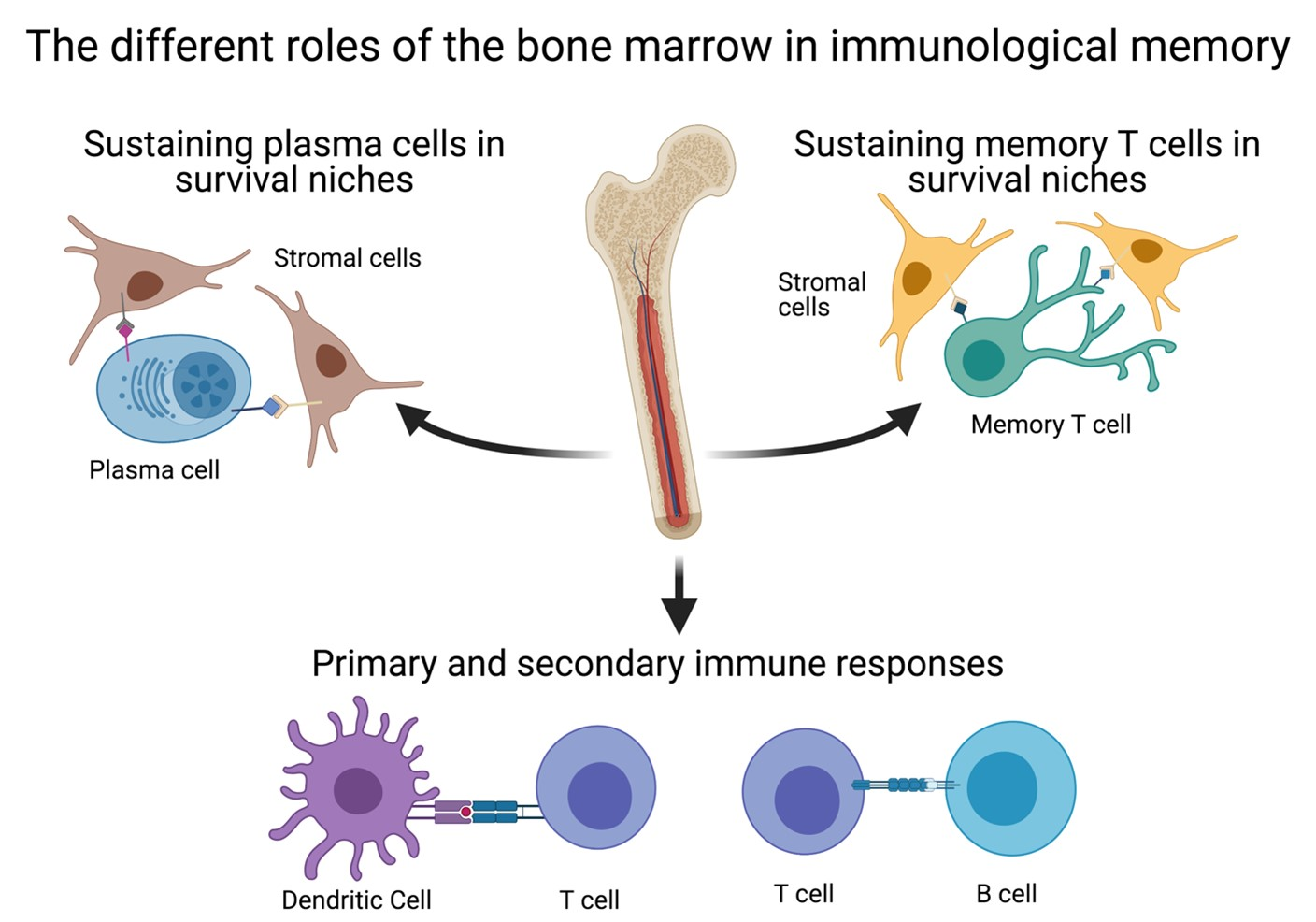
Cells Free Full Text The Bone Marrow As Sanctuary For Plasma Cells And Memory T Cells Implications For Adaptive Immunity And Vaccinology Html
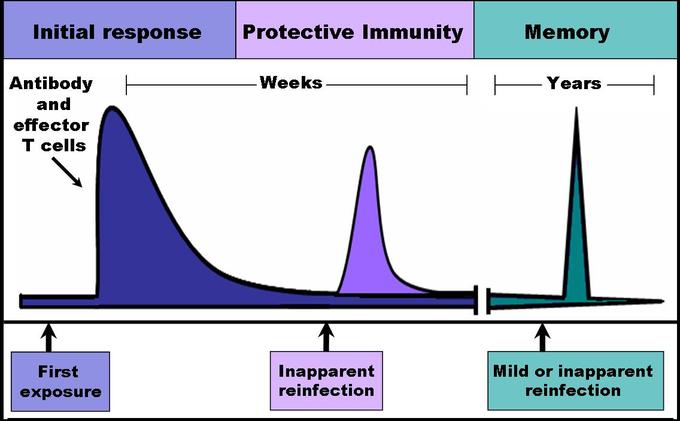
20 6d Immunological Memory Medicine Libretexts

Translating Innate Immunity Into Immunological Memory Implications For Vaccine Development Cell

Cellular Basis Of Immunity Cellular Basis Of Immunity Ms Sneha Singh Department Of Zoology Davcg Yamunanagar Ppt Download
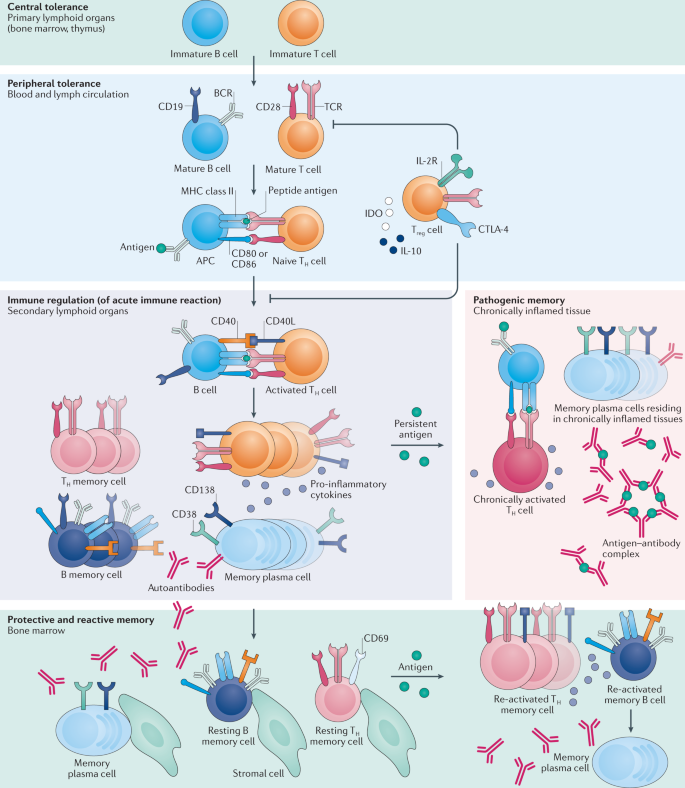
Immunological Memory In Rheumatic Inflammation A Roadblock To Tolerance Induction Nature Reviews Rheumatology

Comments
Post a Comment